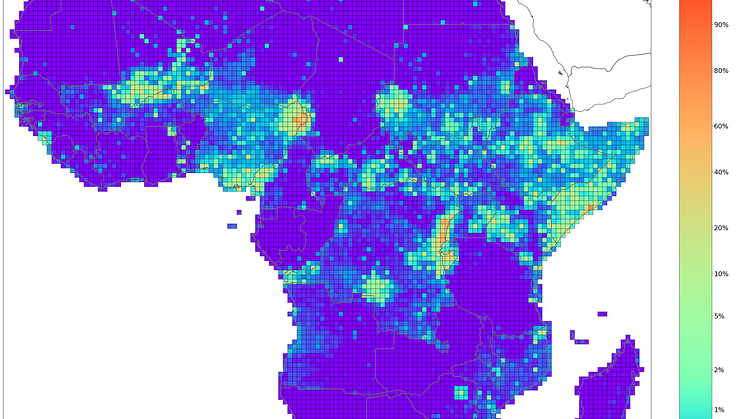
First public forecasts from ViEWS, a political Violence Early-Warning System
The challenges of preventing, mitigating, and adapting to largescale political violence are daunting, particularly when violence escalates where it is not expected. With funding from the European Research Council, ViEWS: a political Violence Early-Warning System is developing a system that is rigorous, data-based, and publicly available to researchers and the international community.