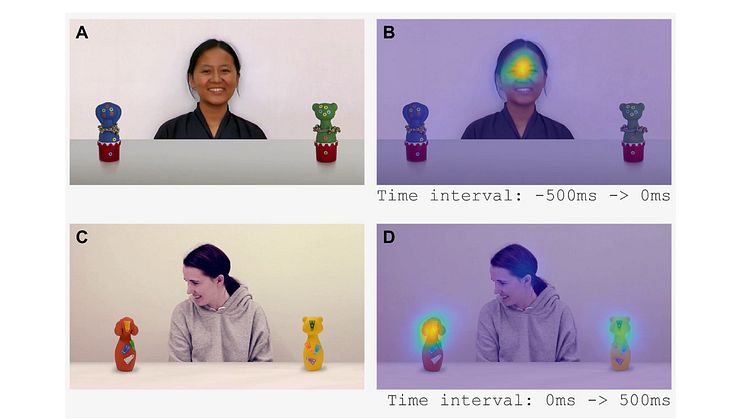
New molecular movie reveals how antibiotic resistance to fusidic acid works
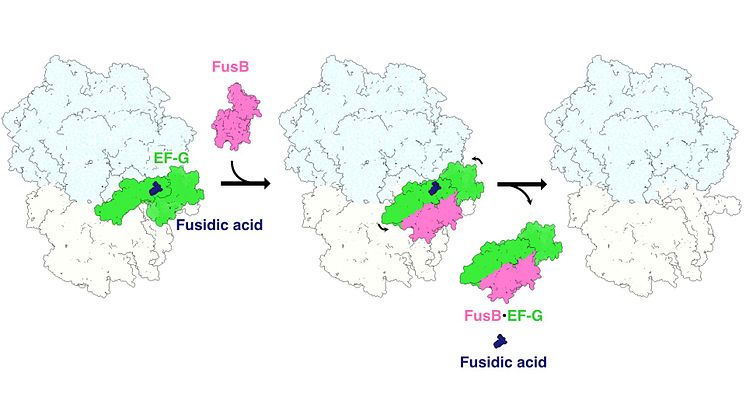
Researchers from Uppsala Antibiotic Center, Uppsala University and SciLifeLab describe a fundamental mechanism of antibiotic resistance. What happens in a bacterium that is resistant to the antibiotic fusidic acid? With a stop-motion movie at the atomic level, they can show that the resistance protein FusB works nearly like a crowbar. Article published in Nature Communications