Controlling starch levels in algae could reduce greenhouse gases
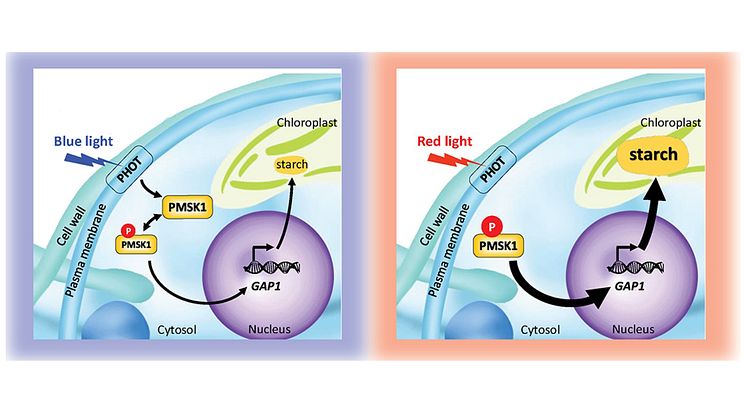
High-starch algae are important in biofuel production, as a feed supplement in agriculture and as an efficient way to bind carbon dioxide. Researchers have now found a new method to control starch storage in algae - a finding with potential applications in areas such reducing greenhouse gases.