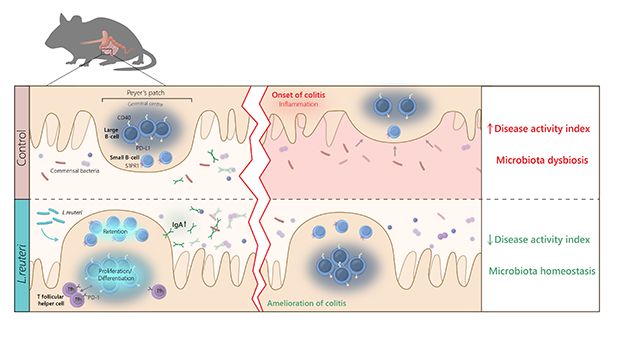
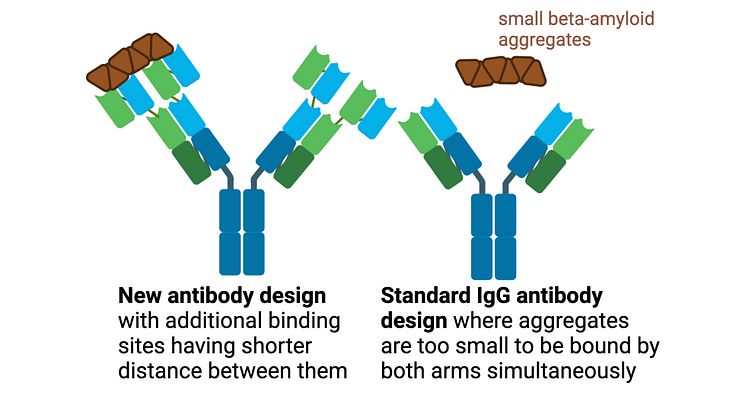
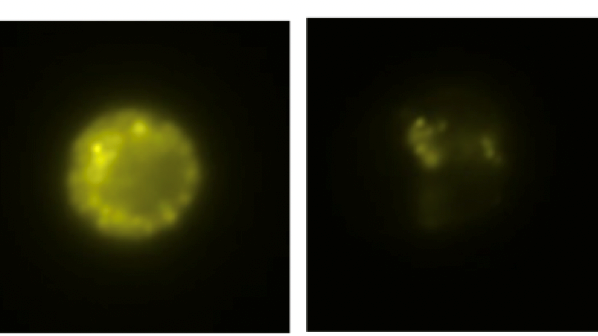
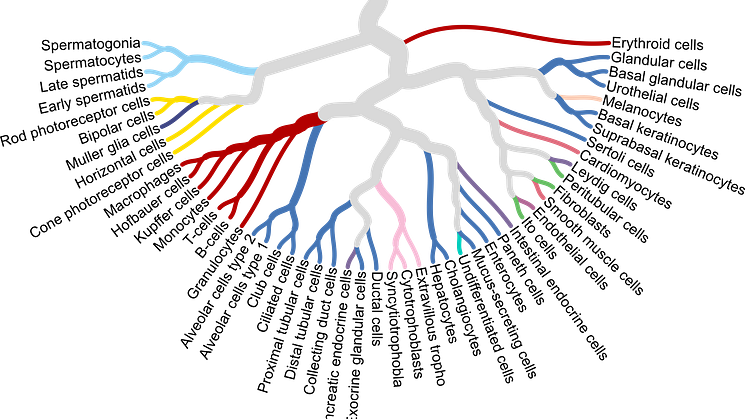
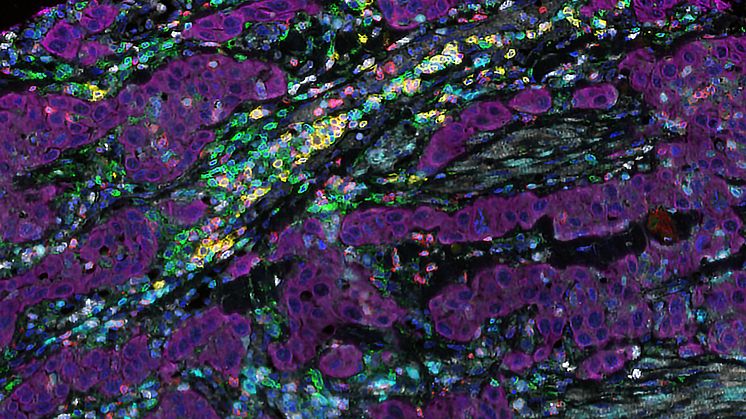
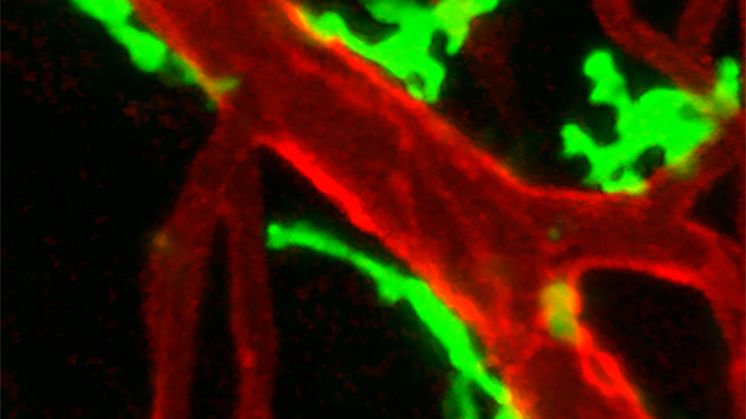
Hunt for the protein TGM1 led to disease discovery
Searching for the protein TGM1 among patients with autoimmune skin diseases, researchers have identified a separate disease that can be linked to autoimmunity against TGM1. This backward method demonstrates a new way of identifying autoantigens as markers for serious diseases. By letting autoantigens point to the disease, diagnosis and treatment can be facilitated, shows study published in PNAS.