New instrument for precision medicine in cardiovascular disease
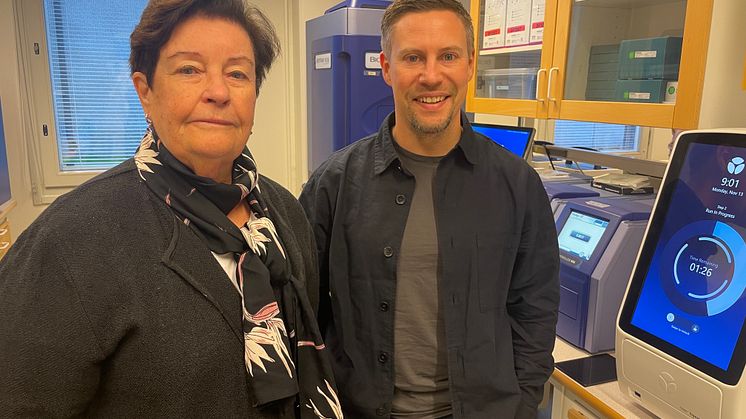
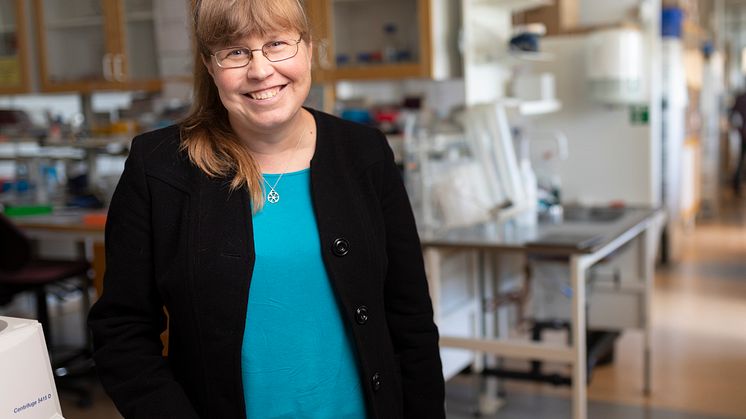
Researchers at Uppsala University have developed an instrument that makes it possible to measure 21 biomarkers for cardiovascular disease simultaneously with great precision by means of a simple blood test. The aim is to use this type of tool to improve the prediction of cardiovascular complications and facilitate more personalised treatment for patients.