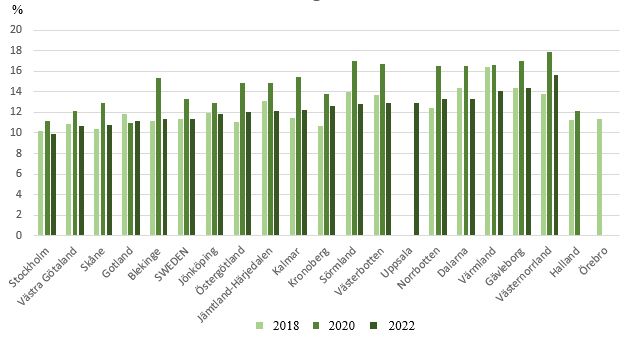
Childhood overweight is associated with socio-economic vulnerability
More children have overweight in regions with high rates of single parenthood, low education levels, low income and high child poverty. The pandemic may also have reinforced this trend. This is shown by a study conducted by researchers at Uppsala University and Region Sörmland in collaboration with Region Skåne.