New mathematical model reveals how major groups arise in evolution
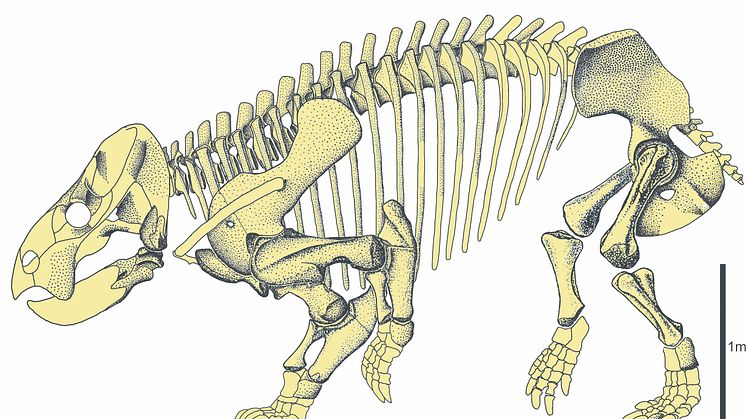
Researchers at Uppsala University and the University of Leeds presents a new mathematical model of patterns of diversity in the fossil record, which offers a solution to Darwin’s “abominable mystery” and strengthens our understanding of how modern groups originate. The research is published in the journal Science Advances.