Genes influence whether infants prefer to look at faces or non-social objects
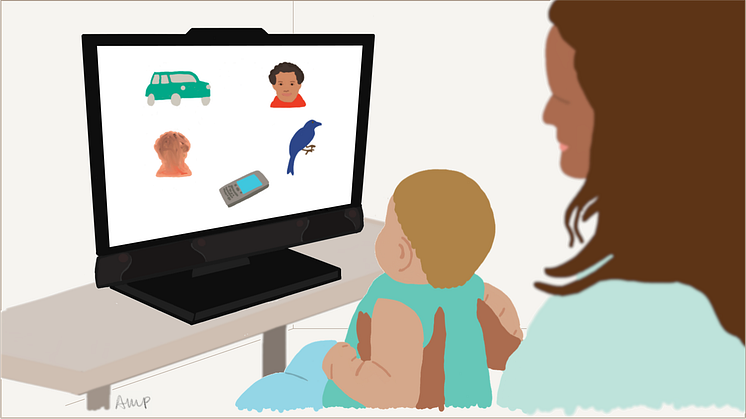
Whether infants at five months of age look mostly at faces or non-social objects such as cars or mobile phones is largely determined by genes. This has now been demonstrated by researchers at Uppsala University and Karolinska Institutet. The findings suggest that there is a biological basis for how infants create their unique visual experiences and which things they learn most about.