Careless cancer cells may be susceptible to future drugs
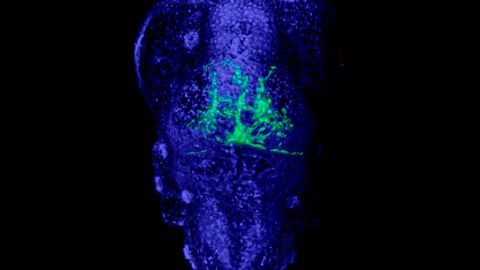
Could the ability of cancer cells to quickly alter their genome be used as a weapon against malignant tumours? Researchers at Uppsala University have succeeded in developing a substance that has demonstrated promising results in experiments on both animal models and human cancer cells. The study is published in the journal Nature Communications.