Increased access to water a threat to nomadic livestock farmers
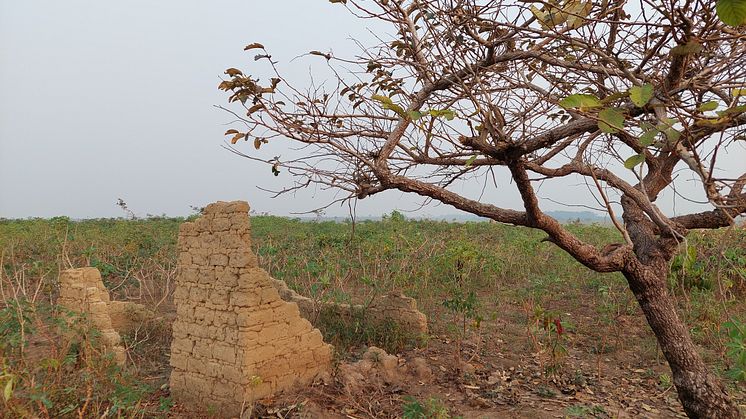
Increasing access to water in extremely arid parts of sub-Saharan Africa can help nomadic livestock farmers in the short term. However, in the long run it may lead to serious consequences for their livelihoods. This is shown by new research from Uppsala University, published in Nature Climate Change.